In the realm of cattle breeding, synchronized fertility through Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) programs is revolutionizing the industry.
In this article we will delve into the multifaceted benefits of implementing such programs, including enhanced breeding efficiency, improved nutritional management, economic gains, and the capacity to adapt to environmental challenges.
We will explore the strategic advantages of synchronized fertility and how it can lead to a more predictable and profitable cattle breeding operation.
Key Takeaways
- Fixed Time AI programs optimize breeding efficiency by synchronizing cattle fertility cycles, leading to more predictable and effective breeding schedules.
- Nutritional management, specifically mineral nutrition, plays a crucial role in the reproductive success and overall health of gestating cows and the beef herd.
- Synchronized fertility programs can lead to significant economic advantages by reducing breeding costs and maximizing the return on investment.
- Implementing early calf weaning strategies during drought and other environmental challenges can help maintain cattle fertility and herd health.
- Small changes in fertility management, such as improving nutrient use efficiency, can have a substantial impact on managing costs and enhancing profitability.
Optimizing Breeding Efficiency with Fixed Time AI
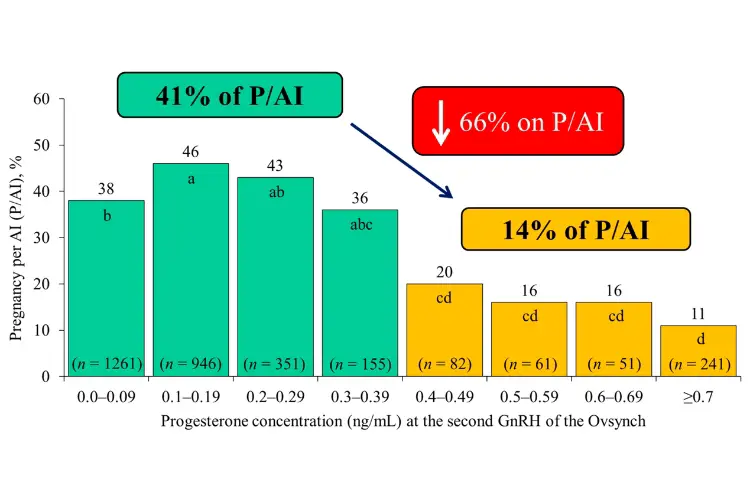
Understanding Fixed Time Artificial Insemination
Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) is a reproductive technology that allows for the precise timing of insemination, independent of the visual signs of estrus in cattle. This method enhances the uniformity of breeding and calving intervals, leading to more predictable and manageable herd management schedules.
FTAI involves synchronizing the estrous cycles of a group of cows so that they can all be inseminated at the same time. This synchronization is typically achieved through the administration of hormonal treatments that regulate the reproductive cycle.
The process of FTAI can be broken down into several key steps:
- Administration of a GnRH analogue to induce ovulation.
- Followed by a prostaglandin injection to regress any existing corpus luteum.
- A second GnRH injection to ensure ovulation occurs uniformly across the treated group.
By controlling the ovulation timing, FTAI reduces the need for continuous observation of estrus behaviors, thereby saving labor and resources. It also allows for the use of superior genetics through artificial insemination, as opposed to relying on natural service which may be less predictable and efficient.
Benefits of Synchronized Breeding Cycles
The implementation of synchronized breeding cycles through Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) presents a multitude of advantages for cattle producers.
A synchronized herd results in a larger proportion of calves born within a narrow timeframe, which simplifies management and enhances the uniformity of the calf crop. This synchronization aligns with the natural estrus cycle of the cattle, ensuring higher success rates in pregnancy.
By concentrating the calving season, producers can more efficiently allocate resources to the care of cows and newborn calves. The following list outlines the key benefits:
- Streamlined calf management and monitoring
- Improved labor allocation during peak breeding and calving periods
- Enhanced ability to implement strategic nutritional programs
- Increased potential for genetic improvement through selective breeding
These benefits collectively contribute to a more predictable and profitable operation, with the potential to significantly impact the bottom line for cattle producers.
Strategies for Implementing Fixed Time AI
Implementing Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) in cattle requires a well-structured approach to ensure the highest success rates. The timing of insemination is critical to achieving high pregnancy rates, as it must coincide with the optimal fertility window of the cows.
To facilitate this, estrus synchronization protocols are employed, which have virtually eliminated the need for heat detection.
A successful FTAI program hinges on several key factors. Firstly, a comprehensive understanding of the herd’s reproductive physiology is essential. This knowledge allows for the customization of synchronization protocols to fit the specific needs of the herd.
Secondly, adherence to a strict schedule is paramount. Any deviation can significantly impact the effectiveness of the program. Lastly, continuous monitoring and evaluation of the program’s outcomes are necessary to make data-driven adjustments for future breeding cycles.
Here is a simple list to guide the implementation of FTAI:
- Evaluate the herd’s reproductive health and history.
- Choose the appropriate synchronization protocol.
- Train staff on the precise timing and technique of AI.
- Monitor and record the results for ongoing improvement.
By following these steps and maintaining a focus on precision and consistency, producers can optimize their breeding operations and enhance overall herd fertility.
Nutritional Management for Enhanced Fertility

Role of Nutrition in Reproductive Success
The intricate relationship between nutrition and reproductive success in cattle cannot be overstated. Third-trimester nutrition is particularly critical, as it sets the stage for a successful calving season.
Adequate mineral intake is essential throughout the gestation period to support not only the developing fetus but also the health and recovery of the cow post-calving. Essential minerals such as zinc, selenium, and copper play pivotal roles in various physiological processes including immunity, tissue repair, and fertility.
Research has shown that supplementing with organic minerals can positively impact pregnancy rates and weaning weights. It is important to ensure that the mineral mix is balanced and tailored to the specific needs of the herd.
Here are some key minerals and their benefits:
- Zinc: Vital for immune function and skin health.
- Selenium: Important for preventing retained placentas.
- Copper: Crucial for iron absorption and overall vitality.
By focusing on the right mineral nutrition, farmers can enhance the reproductive performance of their cattle, leading to a more productive and profitable herd.
Improving Mineral Nutrition for Gestating Cows
Essential minerals play a pivotal role in the health and reproductive success of gestating cows. Adequate mineral intake is crucial not only for the cow’s own well-being but also for the development of the fetus and the subsequent lactation period.
Minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium are vital for tissue repair, immunity, and digestion, all of which contribute to a successful calving season.
To ensure cows receive the right balance of minerals, producers can turn to specially formulated mineral mixes. For example, a mineral higher in magnesium can help prevent grass tetany and support the needs of lactating females. It’s important to choose a mix that complements the forage base and meets the specific requirements of the herd.
Here are some tips for optimizing mineral nutrition:
- Regularly test forage and water sources for mineral content.
- Adjust mineral supplementation based on forage analysis and seasonal changes.
- Provide free-choice mineral feeders to allow cows to consume minerals as needed.
- Monitor body condition scores to ensure cows maintain ideal health throughout gestation.
Nutrition Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Beef Herd

Maintaining a healthy beef herd is crucial for the success of any cattle operation. Proper nutrition is the cornerstone of herd health, especially during the winter and calving season. Lance Kennington, an animal nutrition specialist with CHS, emphasizes the importance of strategic feeding practices to support the herd’s well-being.
A balanced diet is essential for cows, particularly after calving. The post-calving period is when cows have the highest nutrient demands to support lactation and repair the reproductive tract. It’s important to ensure that the diet meets these increased needs to maintain productivity and facilitate recovery.
Here are some key nutrition tips:
- Monitor body condition scores to adjust feed rations accordingly.
- Provide a mineral mix that supports gestation and lactation.
- Consider creep feeding to bolster calf immunity and preserve grazing land during dry conditions.
- Early weaning strategies can reduce forage consumption and support the herd during drought.
Economic Advantages of Synchronized Fertility Programs
Reducing Costs with Efficient Breeding Practices
Implementing Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) in cattle breeding programs can lead to significant cost reductions. By synchronizing the fertility cycles of a herd, producers can better plan and allocate resources, leading to a more streamlined operation.
Efficient use of labor and resources is a key benefit, as FTAI allows for the insemination of multiple animals at a predetermined time, reducing the need for continuous observation and intervention.
One of the primary ways to reduce costs is through the strategic use of fertilizers and nutritional supplements. Small changes in management can improve nutrient use efficiency, which is crucial given the high prices of fertilizers. Below is a list of cost-saving measures that can be implemented alongside FTAI:
- Utilizing cost-effective feed and mineral supplements.
- Implementing early calf weaning strategies to reduce forage consumption.
- Adjusting feeding schedules to optimize growth and fertility.
By adopting these practices, producers can manage their fertility costs more effectively, ensuring the economic sustainability of their operations.
Maximizing Return on Investment

In the realm of cattle breeding, maximizing return on investment (ROI) is crucial for the sustainability and profitability of the operation. By implementing fixed time artificial insemination (AI), farmers can significantly enhance the reproductive efficiency of their herd.
This strategy not only streamlines the breeding process but also ensures that the genetic quality of the offspring is maintained or improved.
One of the key factors in maximizing ROI is the acceleration of age at first calving (AFC). Studies, such as those referenced by the NCBI, indicate that a reduction in AFC can have a positive impact on long-term performance, including longevity and milk yield. This is a clear example of how synchronized fertility programs can lead to substantial economic benefits over time.
To illustrate the potential financial gains, consider the following table which outlines the cost savings associated with reduced calving intervals and improved conception rates:
| Strategy | Cost Savings |
|---|---|
| Reduced Calving Interval | $X per cow/year |
| Improved Conception Rate | $Y per cow/cycle |
By focusing on these areas, farmers can see a direct correlation between the health and efficiency of their breeding program and their bottom line.
Small Changes for Managing Fertility Costs
In the realm of reproductive management, small adjustments can lead to significant savings. By fine-tuning nutritional plans and management practices, producers can enhance nutrient use efficiency and reduce overall fertility costs.
This is particularly relevant in light of high fertilizer prices, which do not necessitate abandoning crop nutrition strategies. One aspect often overlooked is the impact of substances like caffeine on fertility.
Studies have shown that caffeine consumption can affect the hormonal balance, influencing the reproductive endpoints. Therefore, monitoring and potentially moderating caffeine intake in feed could be a cost-effective measure to support reproductive success.
Here are some practical steps to manage fertility costs effectively:
- Review and adjust feed composition to optimize nutritional balance.
- Monitor substance intake, such as caffeine, that may affect fertility.
- Implement regular health checks to ensure early detection and treatment of reproductive issues.
Adapting to Environmental Challenges

Managing Fertility During Drought Conditions
Drought conditions present unique challenges for maintaining cattle fertility. Early weaning is a critical strategy that can significantly reduce daily forage consumption, allowing beef producers to manage cow-calf operations more effectively.
By weaning calves early, the nutritional demands on the cow are lessened, which can be particularly beneficial when resources are scarce. Artificial Insemination (AI) techniques also play a vital role during these times.
Proper AI technique, including understanding reproductive anatomy, ensuring sanitation, and accurate semen deposition, is essential for successful breeding. This is especially true when natural mating may be less feasible due to environmental stressors.
Here are some steps to consider for managing fertility during drought:
- Review and apply best practices for AI, as outlined by resources such as Penn State Extension.
- Implement early weaning to reduce forage demands.
- Adjust nutritional plans to maintain cow health with limited resources.
- Monitor herd fertility closely to make timely decisions.
Early Calf Weaning Strategies
Early weaning of calves is a pivotal strategy during drought conditions, as it significantly reduces daily forage consumption. By weaning calves at a younger age, beef producers can manage their cow-calf operation needs more effectively, conserving limited resources.
Early weaning can also alleviate nutritional stress on the cows, allowing them to maintain better body condition and potentially improve their reproductive performance.
When implementing early calf weaning, it’s important to consider the age and weight of the calves. The seedstock beef industry often adjusts weaning weights to 205 days to make a fair comparison of animals born on different dates.
Older calves normally weigh more, which can influence management decisions. Below is a simple guideline for determining the appropriate weaning time:
- Monitor drought conditions and available forage.
- Assess cow body condition and calf growth rates.
- Plan weaning around the 205-day benchmark for weight comparisons.
- Ensure calves receive adequate nutrition post-weaning to support continued growth.
Adopting these strategies can help producers navigate the challenges of drought, maintaining the health of both cows and calves while optimizing the operation’s overall productivity.
Bolstering Beef Calf Immunity in Dry Seasons

During dry seasons, the challenge of maintaining a healthy beef calf herd intensifies. Nutritional strategies become pivotal in bolstering calf immunity, as traditional grazing may not suffice due to limited pasture availability.
Creep feeding, for instance, can be an effective method to supplement calves’ diet and ensure they receive the necessary nutrients for robust immune development.
Early weaning is another strategy that can be beneficial during drought conditions. By reducing the daily forage consumption, it allows for more effective management of cow-calf operations. Not only does it help in preserving grazing land, but it also contributes to improved weaning rates and potentially increases the return on investment (ROI).
It is important to consider the age of the dam as it can differentially affect the immune response of her calf. Studies have shown that immunoglobulin concentrations, crucial for calf immunity, are reduced in calves born to older dams. This highlights the need for targeted nutritional support for these calves, especially in the first few weeks post-revaccination and booster.
Conclusion
In conclusion, synchronized fertility and fixed-time artificial insemination (AI) breeding programs in cattle offer a multitude of benefits that can significantly enhance the efficiency and profitability of cattle operations. By aligning the breeding season with optimal times for cow health and calf development, producers can ensure ideal body condition, high-quality colostrum, and healthy calves.
The predictability afforded by these programs aids in better planning and resource allocation, as seen in successful winter calving seasons. Moreover, during challenging conditions such as drought, these strategies can be pivotal in managing forage consumption and maintaining herd health.
The integration of nutrition and mineral intake, along with careful management of fertility costs, further supports the success of these programs. Ultimately, synchronized fertility and fixed-time AI breeding programs are powerful tools that, when implemented with precision and care, can lead to a more sustainable and profitable future for the beef industry.
FAQs:
What is Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) in cattle?
Fixed Time Artificial Insemination (FTAI) is a reproductive management practice that involves synchronizing the estrous cycles of a group of cows and then inseminating them at a predetermined, fixed time without the need to detect estrus in each individual cow.
How does synchronized breeding benefit cattle operations?
Synchronized breeding can lead to more uniform calf crops, efficient use of labor since the timing of breeding is controlled, and potentially improved pregnancy rates. It also allows for better genetic management through the use of superior sires.
What nutritional strategies can enhance fertility in cattle?
Maintaining ideal body condition, providing balanced mineral nutrition, and ensuring adequate energy intake are critical for enhancing fertility. Proper nutrition supports immunity, gestation, lactation, and overall reproductive success.
How can synchronized fertility programs reduce breeding costs?
By synchronizing fertility, producers can reduce the labor and time spent on heat detection, optimize the use of AI resources, and improve the overall efficiency of the breeding process, leading to potential cost savings.
What are some strategies for managing fertility during drought conditions?
During drought, strategies like early calf weaning can reduce forage needs, while nutritional adjustments can help maintain herd health. It’s also important to manage breeding schedules to ensure cows are in optimal condition for pregnancy.
Can synchronization and FTAI programs be adapted for different environmental challenges?
Yes, synchronization and FTAI programs can be tailored to fit various environmental conditions by adjusting the timing of breeding, nutritional support, and management practices to ensure the highest chance of reproductive success.


